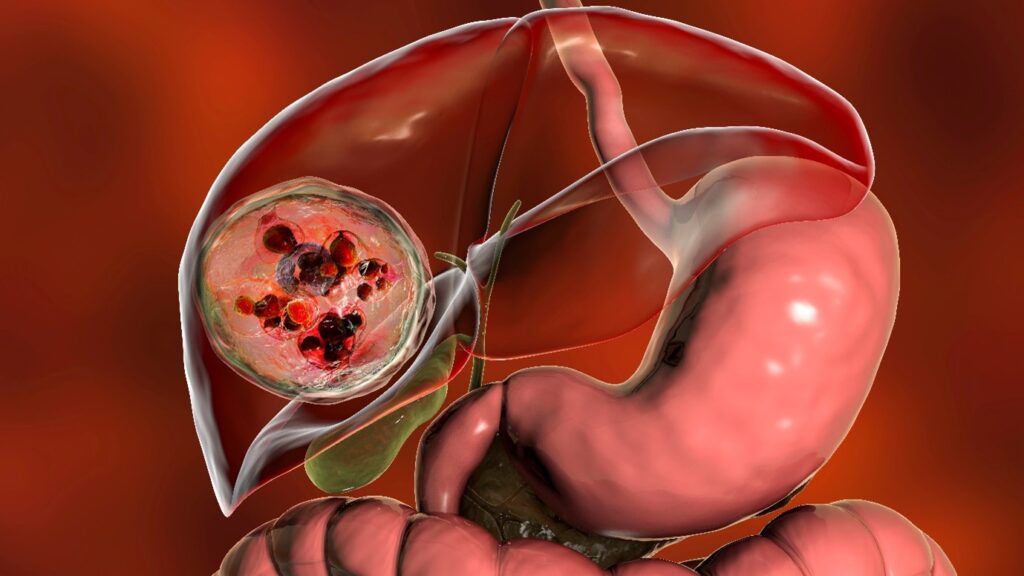
Hydatid disease, or cystic echinococcosis, is a serious parasitic infection caused by tapeworms, typically found in sheep and dogs.
What is Hydatid Disease?
Hydatid disease is caused by tapeworms in the genus Echinococcus. The parasite’s eggs are found in the stools of infected animals, primarily dogs, and can be transmitted to humans if ingested.
Once inside the body, the eggs develop into fluid-filled cysts, most commonly in the liver or lungs, but they can affect other organs too. If untreated, these cysts can lead to severe complications.
Who is at Risk for Hydatid Disease?
People living in rural or poor areas, especially those raising livestock, are most at risk.
Sheep, the primary hosts of the parasite, transmit the infection to dogs, who then pass the parasite to humans through fecal contamination.
High-risk activities include handling infected dogs, eating or drinking in areas with poor hygiene, or slaughtering sheep.
What are the Symptoms and Complications?
Hydatid disease can remain asymptomatic for years, but as cysts grow, symptoms may develop. Common signs include:
- Abdominal discomfort or a lump in the midsection
- Coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain
- Jaundice or skin rash
- Nausea, vomiting, and weight loss
In severe cases, cysts may rupture, causing life-threatening reactions like anaphylaxis, severe abdominal pain, or even sudden death. Without treatment, organ failure can occur, and untreated cases may be fatal.
How is Hydatid Disease Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosis is made through blood tests that detect antibodies and imaging techniques like
- X-rays
- CT scans
- Ultrasounds
These tests reveal the size and structure of the cysts, distinguishing them from simple liver cysts.
Treatment varies depending on the size and location of the cysts. Common approaches include:
- Medications: For smaller, superficial cysts, antiparasites, which shrink cysts and kill the parasites, can be used.
- PAIR (Puncture, Aspiration, Injection, Re-aspiration): A procedure where the cyst is drained and treated with anti-parasitic chemicals.
- Surgery: Larger cysts may require surgical removal, which carries the risk of spreading parasites.
How Can Hydatid Disease Be Prevented?
Preventing hydatid disease centres on reducing exposure to infected animals and contaminated environments. Key prevention tips include:
- Deworm pets regularly with a veterinarian’s help.
- Avoid handling infected dogs or consuming contaminated food and water.
- Wash hands and vegetables thoroughly before eating.
- Do not slaughter livestock at home.
- Ensure proper sanitation in environments with livestock and pets.
Stay Safe and Be Aware
Hydatid disease can lead to severe health complications if left untreated, but it’s preventable with proper hygiene and precautions. Stay informed, protect yourself, and consult a healthcare provider if you suspect an infection. Your health is worth it!
For more information and expert advice, contact your healthcare provider today.